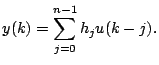
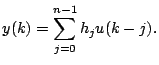
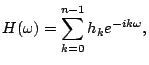
In this section, we consider the minimax dB linear phase lowpass FIR filter design,
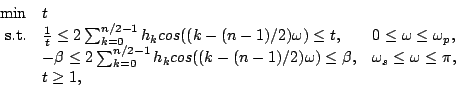
Note that this problem has infinite constraints. Subsequently, we
discretize the frequency parameter ![]() to obtain a
finite-constraint approximation. Moreover, there is a nonlinear
term
to obtain a
finite-constraint approximation. Moreover, there is a nonlinear
term
![]() in the first part of the constraints. To
convert it to a second order cone constraint, we introduce
in the first part of the constraints. To
convert it to a second order cone constraint, we introduce ![]() such that
such that
Now, we obtain the problem in SOCP form,
Example 5. Given
![]() ,
,
![]() , and
, and
![]() We descretize the frequency parameter
We descretize the frequency parameter ![]() by the uniform step
by the uniform step
![]() We choose
We choose
![]() as our test samples.
as our test samples.
More details about this problem and the interior point approach can be found in [19].