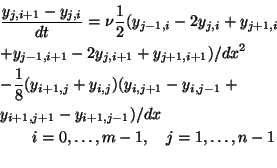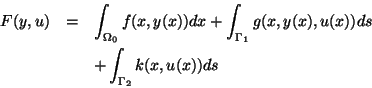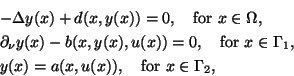

Next: Known SSC Results for
Up: Sufficient Optimality for Discretized
Previous: Introduction
Parabolic and Elliptic Control Problems
In this section we describe the continuous control problems
exemplarily considered in the following. The first is a
one-dimensional parabolic boundary control problem formulated such that it
includes problems from [1,9] and has additional
pointwise state constraints.
minimize
subject to(P)
The notation above is that of [1] and the corresponding data will
be defined in section 5 below. The problem does, however, include
also one considered in [9], namely by choosing 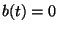 ,
,
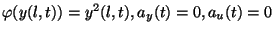 .
.
We define the following discretization of problem (P).
subject to(P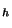 )
)
Here 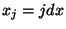 ,
,  ,
, 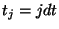 ,
, 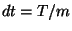 .
.
For the problem (P) above and specific data an analytic solution is given in
[1] and this also permits the authors to verify the necessary and
sufficient optimality conditions they had stated and proved.
Next, we consider the instationary Burgers equation
which we discretize by
For the elliptic control problems we consider the class defined in
[18]. It includes boundary and distributed controls which are
addressed separately in [16], respectively [17] as well
as Dirichlet, Neumann, and mixed boundary conditions. In the case of boundary
control the underlying continuous problem is
minimize
subject to(EB)
and
Here 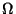 is a bounded, plane domain with piecewise smooth boundary
is a bounded, plane domain with piecewise smooth boundary
 .
.
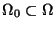 is equal to
is equal to 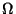 unless noted
otherwise.
unless noted
otherwise. 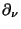 denotes the derivative in the direction of the
outward unit normal
denotes the derivative in the direction of the
outward unit normal  on
on  and the boundary is partitioned as
and the boundary is partitioned as
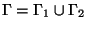 with disjoint sets
with disjoint sets
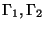 consisting of finitely many connected components. For the general
formulation given above in [17,18] necessary optimality
conditions are stated, a discretization is described in full detail and the
corresponding optimality conditions are related carefully to those for the
continuous problem. With concrete applications in mind then, however, the
following data of the problem are specialized, the objective function
consisting of finitely many connected components. For the general
formulation given above in [17,18] necessary optimality
conditions are stated, a discretization is described in full detail and the
corresponding optimality conditions are related carefully to those for the
continuous problem. With concrete applications in mind then, however, the
following data of the problem are specialized, the objective function
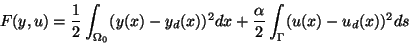 |
(2.1) |
with 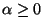 and the inequality constraints
and the inequality constraints
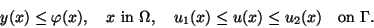 |
(2.2) |


Next: Known SSC Results for
Up: Sufficient Optimality for Discretized
Previous: Introduction
Hans Mittelmann
2000-08-31
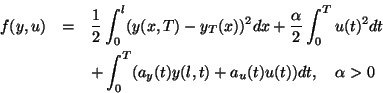
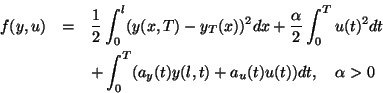
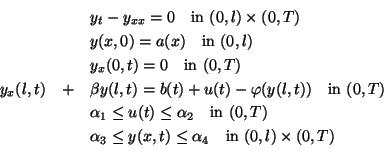
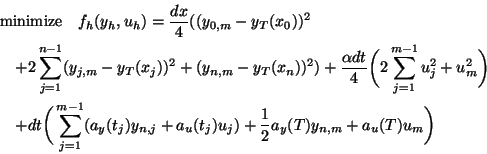
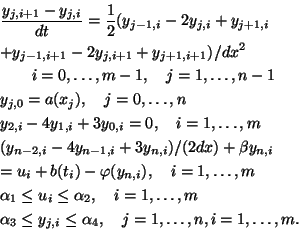
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.