Global Optimization
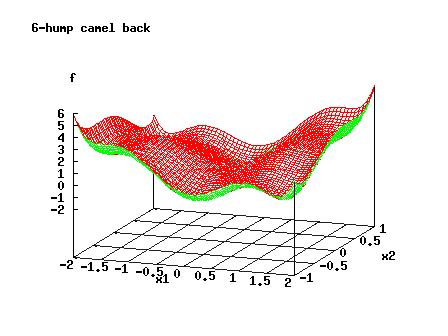
The occurrence of multiple extrema makes problem solving in nonlinear optimization even harder. Usually the user dreams of the global (best) minimizer, which might be difficult to obtain without supplying global information, which in turn is usually unavailable for a nontrivial case. The following picture shows the function
f(x,y)=x^2*(4-2.1*x^2+x^4/3)+x*y+y^2*(-4+4*y^2)
which has two global minima at (0.09,-0.71) and (-0.09,0.71) and four additional local minima.
The Unconstrained NLO-Problem:
min f(x), n=dim(x).
Global optimization is a difficult area, at least for larger n, since there is no easy algebraic characterization of global optimality.
Most of the codes designed for minimization simply restrict themself to solve the equation grad(f(x))=0, which is only necessary of course.
Methods using interval-arithmetic and branch&bound will in principle solve these problems, but the branch tree might become excessively
large for difficult functions. Hence for higher dimensions and without special structure only stochastic or pseudostochastic methods
will apply.
See however the books of Kearfott
Rigorous Global Search: Continuous Problems
Kluwer, Dordrecht 1996, Floudas
Deterministic Global Optimization: Theory, Algorithms and Applications
, Kluwer, Dordrecht 1999, and Hansen&Walster
Global Optimization Using Interval Analysis
, Marcel Dekker 2003. See A. Neumaier's
paper
on methods and softwares
Mostly stochastic or heuristic search methods have been available freely, but this has changed, see below for constrained optimization.
| DFL | A library of algorithms for derivative free (global) optimization (f90, C, Julia) |
| PANMIN | Two stochastic methods, one MPI parallelized; uses Merlin/MCL |
| BTRK | f90-version of the derivative-free Boender-Timmer-Rinnoy Kan algorithm |
| PSwarm | Hybrid derivative-free solver (particle swarm & direct search), AMPL interface (C (also parallel), Matlab) |
| MEMPSODE | Hybrid derivative-free solver (particle swarm & local search); uses Merlin/MCL |
| netlib/toms/667 | method of Zirilli et al (stochastic differential equation approach) |
| GANSO | several methods for global&nonsmooth problems (C/C++) |
| netlib/opt/simann | simulated annealing (f77) |
| simannf90 | f90-version from Alan Miller |
| simann.m | Matlab version |
| Java-SA | Java implementation of SA |
| Simanneal | Python implementation of SA |
| CSA | Python implementation of coupled SA |
| ASA | C, adaptive simulated annealing, Python interface |
| CMA-ES | Evolution Strategy with Covariance Matrix Adaptation (Matlab) |
| PGSL | A direct stochastic algorithm for global search incl constraints (C) |
| Fortran-GA | genetic algorithm |
| PIKAIA | genetic algorithm; IDL, f90, parallel versions Excel version |
| DGPF | Distributed Genetic Programming Framework. needs Eclipse for compile |
| SIGOA | Simple Interface for Global Optimization Algorithms, Java source |
These methods are simple to use, but require a high number of function evaluations if you desire acceptable final precision. Here are codes which determine the global minimum of a Lipschitz continuous function on a finite box:
| DIRECT ( f77, Matlab, C, Julia) | using a bound for the Lipschitz constant of f and subdivision |
| MCS | Huyer&Neumaier's Multilevel Coordinate search, local search by SQP, Matlab |
The following codes fit a surrogate model to an expensive to evaluate function of few variables and analyze/minimize that:
| SPACE | global optimization through meta-modeling: fitting, cross-validation, prediction, minimization (C++) |
| Spacemap | Optimization using Surrogate Models (Matlab) |
The Constrained NLO-Problem:
min f(x) subject to h(x)=0, g(x)>=0,
n=dim(x), m=dim(g), p=dim(h).
Few codes are available but this is an area of current research and more links will be added. See also the book by Eldon Hansen, Global Optimization Using Interval Analysis, Dekker, New York, 1992.
For a good introduction into the theory see the book by Horst et al. For the state of the art until 1994, see the Horst&Pardalos handbook. An application-oriented overview is given in this book by Floudas. An introduction is given by Liberti and recent survey papers on the mixed-integer case are Burer et al and Belotti et al
| Black Box Opt | Black box functions and constraints, expensive evaluations, no derivatives needed (C, GPL) |
| GloptiPoly | Polynomial objective and constraints, integer variables, needs SeDuMi (Matlab, GPL) |
| SOSTOOLS | Matlab toolbox to solve sum of squares polynomial problems; needs SeDuMi and Matlab's symbolic toolbox (GPL) |
| INTLAB | Matlab toolbox for self-validating algorithms |
| DIRECT | version of DIRECT that handles general constraints using L1 penalty (Matlab) |
| GlobSol | Interval software, f90, book, exhaustive search, automatic differentiation, bound and equality constraints, nonlinear systems, sources, needs several local optimizers and linear algebra routines plus the author's interval package |
| VerGO | C++, interval branch&bound, bound constraints, automatic differentiation, self-contained |
| Genocop | various versions, including for nonlinear constraints (C) |
| PGSL | A direct stochastic algorithm for global search incl constraints (C) |
| BARON | solves variety of global problems deterministically including discrete, free demo version from GAMS |
| COUENNE | solves continuous and discrete global problems deterministically, C++ |
| SCIP | solves continuous and discrete global problems deterministically, C |
| Maple GOT | toolbox containing both B&B and random methods |
For more information on global optimization, see GLOBOPT