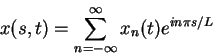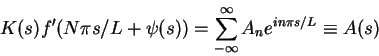

Next: Computer simulations
Up: No Title
Previous: Introduction
We consider here only the case where
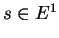 and
and
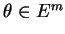 where
where
 to illustrate
several interesting features of such systems.
The general case can be treated in similar ways.
to illustrate
several interesting features of such systems.
The general case can be treated in similar ways.
The observables of this system are usually
not 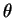 ,
but some
periodic wave form
or function of
,
but some
periodic wave form
or function of 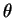 such as
such as
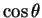 or
or
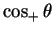 .
This suggests that we seek a steady progressing wave solution
in the form
.
This suggests that we seek a steady progressing wave solution
in the form
where 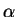 is called the wave number
and c is a vector of wave speeds.
is called the wave number
and c is a vector of wave speeds.
Direct substitution of the steady progressing wave
solution into the equation gives
There is a unique constant solution of this equation for cprovided the components of 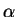 have
the form
have
the form 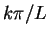 for some integer
for some integer
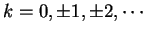 .
.
Let us fix
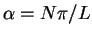 for some integer N. According to the calculation above,
there is a steady progressing wave solution of the system
having the form
for some integer N. According to the calculation above,
there is a steady progressing wave solution of the system
having the form
where cN is given by the formula
To test the stability of this steady
progressing wave we define
The result is
Expanding the right hand side in powers of 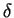 and ignoring higher order terms gives
and ignoring higher order terms gives
Expanding x in its Fourier series
and substituting this into the equation gives
where
Thus, depending on the properties of the
coefficients in A, we get the following
stability results for the
deviation x: If
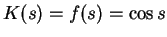 and
and
 ,
then the leading components of x are harmonic and the remaining
modes are damped. If
,
then the leading components of x are harmonic and the remaining
modes are damped. If
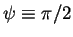 ,
then all modes (except for n=0) are damped.
,
then all modes (except for n=0) are damped.


Next: Computer simulations
Up: No Title
Previous: Introduction
Hans Mittelmann
2000-04-04
![]() ,
but some
periodic wave form
or function of
,
but some
periodic wave form
or function of ![]() such as
such as
![]() or
or
![]() .
This suggests that we seek a steady progressing wave solution
in the form
.
This suggests that we seek a steady progressing wave solution
in the form
![]() for some integer N. According to the calculation above,
there is a steady progressing wave solution of the system
having the form
for some integer N. According to the calculation above,
there is a steady progressing wave solution of the system
having the form
![]() and ignoring higher order terms gives
and ignoring higher order terms gives